Treatment of Male Erectile Dysfunction
Regenerative medicine is a relatively young field in the treatment of various conditions. Several novel applications of various types of stem cells have been tried and applied in various aspects of urology. Some published articles provide promising early results.
There are two main sources of stem cells. These are embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and adult-derived stem cells (ADSC). The latter has many sources including bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs), skeletal-muscle-derived stem cells (SkMSCs), adipose-tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs), and arguably, amniotic-fluid-derived stem cells (AFSCs).
Stem cell use in urology:
BMSCs, SkMSCs, and AFSCs have been used for bladder augmentation and detrusor regeneration in animals. SkMSCs are the only stem cells to have been successfully tested in humans, for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. ESCs, BMSCs and SkMSCs have been shown to improve erectile function in animal models. Both ESCs and BMSCs can be differentiated into sperm and, remarkably, the ESC-derived sperms have generated offspring in mice.
Adipose-derived stem cells:
ADSC research is a relatively young field, and these cells are largely unstudied in urology. However, as a result of their high differentiation potential and ease of isolation, ADSCs represent an exciting resource for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine within and beyond urology.
ADSC’s need a target tissue to reach and excerpt their regenerative action. Signals are needed from the affected tissue to attract them.

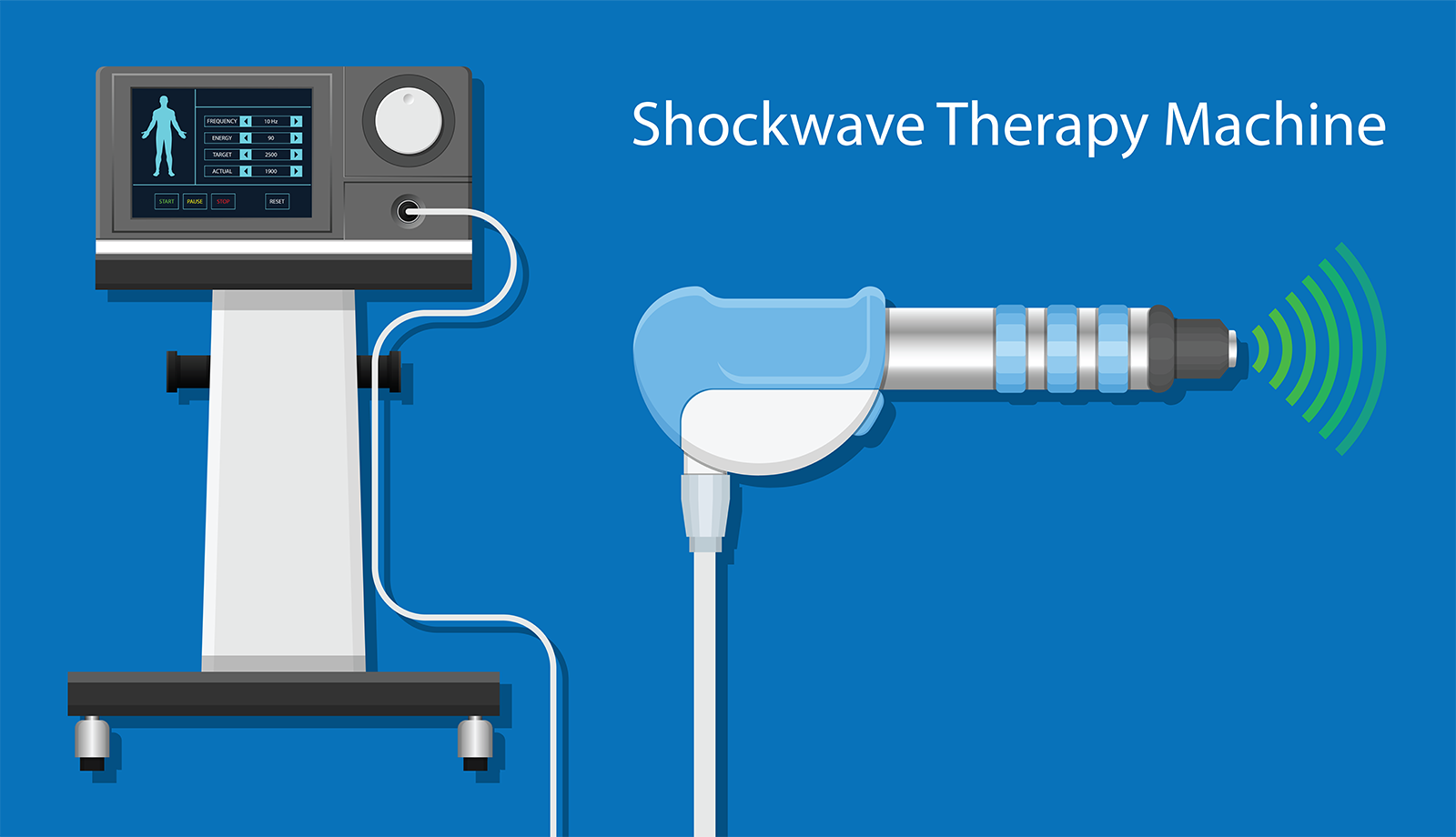
Low-Intensity Shock Wave Therapy (Li-ESWT)
This relatively new modality of treatment is gaining acceptance with encouraging intermediate-term results, as proven with their approval as part of the urology guidelines.
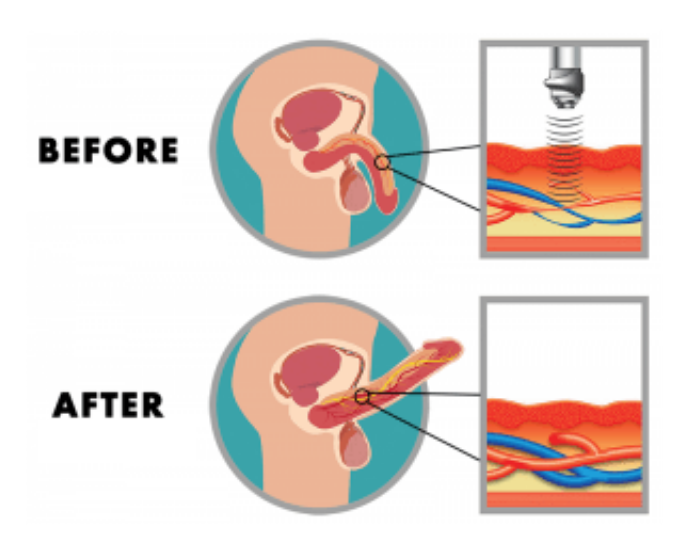
Shock waves appear to induce micro trauma to the tether tissue hence, stimulate vascular flow and erectile function and one possible mechanism of action are through an endogenous stem cell-mediated regenerative effect. This micro trauma not only stimulates the local regenerative process, but the resultant signals act as a lighthouse for the ADSC’s to reach and synergistically enhance the local regenerative and repair process in the penile corpora.
Evidence:
Elliot Lander and Mark Berman reported a case series whereby 52 patients with Erectile Dysfunction received a concurrent combination of Li-ESWTand intracavernosal injection of autologous SVF (rich in MSCs and HSCs) from human lipoaspirate.
Initially SVF was harvested via liposuction and sent for preparation. Patients received Li-ESWT while awaiting the SVF preparation process. Then a tourniquet was applied to the base of the penis and 10 cc of SVF was injected into one side of the corpora cavernosa. The tourniquet was removed after 20 min.
Overall, 37 out of 52 patients (71%) reported an improvement in erectile function after combined SVF and Li-ESWT. None of the other fifteen patients reported worsening of their erectile function after treatment.
Future studies are needed in the form of placebo randomized trials to better establish the effects of stem cells combined with shock waves on Erectile Dysfunction.